In the intricate mechanism of finance, the shadows of money laundering and terrorist financing loom large. The imperative for financial institutions and businesses is clear – a vigilant and responsive stance towards Anti-Money Laundering (AML) red flags.
This blog will lead you through the types of AML red flags, their origins, and how to deal with them.
Why is AML Compliance Important?

AML compliance not only imposes a mandate for robust due diligence processes but also assumes a pivotal role in weaving the reputation fabric of businesses and financial institutions, safeguarding against money laundering and other illicit activities, and cultivating a culture of ethical business practices. It also makes sure that financial transactions happen openly and follow the laws and rules set by regulators.
Read more:
- KYC and AML: Key Differences and Best Practices
- Anti-Money Laundering Checks Explained: Everything You Need to Know
- What is a customer identification program (CIP)?
What are Red Flags in Money Laundering?
AML red flags are behavioral patterns that indicate illicit financial activities. Recognizing these warning signs often becomes the key to bolstering your defense against money laundering and terrorist financing. Here, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) orchestrates AML guidelines for identifying red flags and responding to red flags with precision.
The Role of the FATF
The FATF, an intergovernmental body, provides international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing. By issuing red flag indicators, the FATF helps financial institutions and businesses identify potential risks of money laundering and take necessary actions to mitigate them.
FATF’s Red Flag Indicators
The FATF has outlined 42 red flag indicators categorized into four groups. Understanding these red flag indicators is crucial for building an effective compliance framework against money laundering.
Category 1: Red Flags About the Client
1. Secrecy/evasiveness: Customers providing incomplete or suspicious information
Engaging with clients who withhold crucial information can pose serious risks. Clients evading details about their identity, beneficial ownership, funding sources, or transaction motives raise significant concerns. The FATF emphasizes the importance of Know Your Customer (KYC) checks, Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) procedures to address this issue. Implementing robust measures ensures that new customers furnish necessary information verified through official documents.
2. Fake documents: Use of unusual or suspicious identification documents
Vigilance is key when dealing with clients possessing questionable personal histories characterized by criminal activity or any other illicit action. Companies should exercise heightened scrutiny for clients with criminal convictions or connections to illegal activities, extending this caution to their relatives. The use of suspicious or illegal funds or unusual identification documents for business transactions is a red flag that warrants immediate attention.
3. Unusual transactions: Customers engaging in one or multiple currency transactions of a large, frequent, or unexplained nature
Unusual transaction patterns demand careful observation. Customers involved in large, frequent, or unexplained transactions should trigger suspicion. This includes withdrawing large sums regularly without a clear economic purpose, depositing unusually large amounts of private funding, other suspicious transactions, and engaging in unusual transactions with multiple accounts or bank or foreign accounts without a valid explanation. Establishing comprehensive transaction monitoring policies, often automated for efficiency, coupled with KYC checks, helps identify and mitigate such a red flag.
Category 2: AML Red Flags in the Source of Funds
1. Inconsistent economic profile: Sudden changes in currency transaction patterns
Sudden changes in currency transaction patterns signal a potential red flag. Clients conducting unusual cash transactions, such as frequent large withdrawals or cash deposits, especially in cash, should be thoroughly examined. Implementing robust transaction monitoring policies, augmented by automated solutions and KYC checks, becomes imperative in detecting and addressing these patterns effectively.
2. Unexplained Cash Collateral: Large volumes of checks or fund transfers to multiple bank accounts without reasonable explanation or clear justification
Large volumes of cashier’s checks or fund transfers without clear justification pose a significant risk. The inability to provide a legitimate source for these funds, especially in dealings with high-risk entities, demands careful scrutiny. The FATF Typologies Report provides valuable insights into identifying such red flags.
3. Unverified Source of High-Risk Funds: Funds transfers lacking transparency or a clear source
The transparency of funds is crucial. The FATF report emphasizes the need to scrutinize third-party funding without apparent connections, funds from foreign countries lacking clear ties, and funds from high-risk countries. Thorough assessment and verification of the source of funds are essential to prevent potential money laundering risks.
For further exploration of source-related red flags, delve into our blog on AML Risk Assessment.
Category 3: Red Flags in the Choice of Lawyer
1. Instructions from an unrelated or inexperienced legal professional: Legal counsel involvement lacking legitimacy
Clients choosing legal services from representatives unfamiliar with industry-specific regulations or residing in different countries raise concerns. This mismatch in the legal services’ counsel and client needs could indicate a potential red flag that warrants a deeper examination.
People typically hire legal representatives that correspond to their needs. That’s why if a client chooses a lawyer who’s not familiar with their industry-specific regulations or doesn’t reside in the same country, it can be considered a red flag.
2. Willingness to pay unusually high fees: Indication of potentially more suspicious activity in transactions
Clients expressing a willingness to pay significantly higher fees, especially in very large cash transactions, between different accounts should be viewed with suspicion, thereby getting categorized as a red flag. This behavior may indicate an attempt to obscure the source of funds or the true nature of their activities, necessitating a closer look to ensure compliance with anti money-laundering laws.
3. Multiple changes in legal consultants: Frequent alterations in legal representation
Frequent changes in legal representation, especially without apparent justification, raise concerns. This could be a deliberate strategy to evade detection by authorities or distance themselves from previous suspicious activities, highlighting the importance of sustained scrutiny.
For a more comprehensive understanding of legal-related red flags, visit our blog on AML policy.
Category 4: Red Flags in the Nature of the Retainer
1. Disinterest or desire for shortcuts: Indication of potential misconduct
Clients exhibiting disinterest in their legal case or expressing a desire for shortcuts may signal a higher risk of potential misconduct. Such behavior could be a red flag for possible money laundering activity or other illicit activities, requiring thorough compliance procedures to assess and mitigate associated risks.
2. Complex ownership structure: Lack of valid reasons or involving multiple countries
Complex ownership structures involving multiple jurisdictions or shell companies raise suspicions, indicting a financial crime. This lack of transparency makes it challenging to identify the true beneficial owners and may facilitate money laundering activities. Vigilance is crucial to assess the source of funds and associated risks.
3. Multiple stock purchases with common elements: Unusual patterns in securities transactions
Unusual patterns in stock purchases, such as multiple purchases of the same stock by seemingly unrelated entities, may indicate financial crimes like market manipulation. This red flag can artificially inflate stock prices or disguise the movement of illicit funds, emphasizing the need for vigilant monitoring and assessment.
For a deeper exploration of retainer-related red flags, explore our blog on transaction monitoring in AML.
Industry-wise AML Red Flags
AML red flags can vary across industries. It’s essential to understand specific indicators based on the sector. Here are some industry-specific AML red flags:
Crypto Industry
In the crypto industry, unique challenges demand heightened scrutiny:
Unusual size, destination, or pattern of transactions
- Use of mixing services and fraudulent exchanges
- Breaking down large transactions into smaller ones (structuring)
- Suspicious user behavior (constant change of personal information)
Read more about and how to track and submit suspicious activity reports.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions encounter distinct risks in the realm of financial crime and money laundering havens to AML. Understanding the international watchlist screening is crucial for ensuring robust AML measures and understanding a red flag encountered in the processes with financial institutions. There are three money laundering stages:
- Placement: Introducing illicit funds into the financial system.
- Layering: Conducting complex financial transactions to obscure the source of illicit funds.
- Integration: Returning illicit funds to criminals in a manner that appears legitimate.
Read more:
- What is Smurfing and How You Can Prevent it Proactively
- What is a money mule?
Real Estate
Real estate transactions are susceptible to money laundering in the following ways:
- Anonymous buyers and use of shell companies
- Buyers or funds in countries with weak AML regimes or high corruption
- Discrepancy between buyer’s income and property value
- Unexplained distance between buyer and property
- Under- or overpriced property value
- Large amounts of cash used
Traders and Brokers
Trading and brokerage businesses must remain vigilant against suspicious activity and potential financial crimes. Proactive measures are crucial to combat illicit activities in financial institutions. Red flags for suspicious activity in this industry include:
- Quick movement of money with low daily balances
- Foreign exchange transactions
- Large transfers from customers without a trading background
Explore proactive measures to ensure a fortified stand against a financial red flag.
Read more: What is Trade Based Money Laundering (TBML)?
Combat Money Laundering and Financial Crime Proactively With HyperVerge
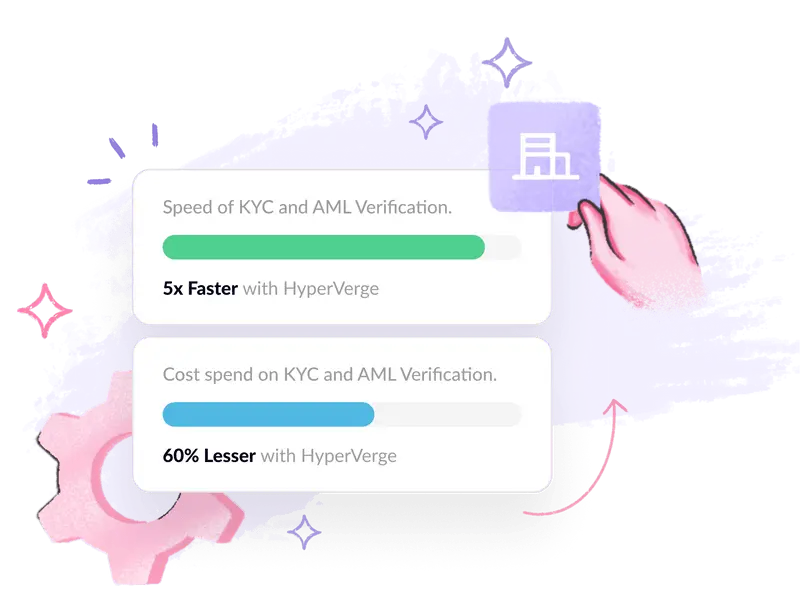
To combat money laundering effectively, financial institutions and businesses must adopt a robust AML compliance program. Implementing advanced AML software, like HyperVerge’s AML solution, can enhance your AML compliance efforts.
HyperVerge can help you with:
- Global sanctions screening and watchlists check
- Politically Exposed Person (PEP) screening
- Adverse Media screening
- Continuous monitoring
- And more.
Want to see it in action? Sign up for free today.






